Learn when to apply for FDA Orphan Drug Designation (ODD), key considerations, and strategies for fast-tracking rare disease drug development.
In the fast-evolving landscape of drug development, obtaining a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) special designation such as Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) can significantly accelerate the development process for treatments targeting rare and serious diseases. For life science companies, obtaining Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) can accelerate the path to market for a promising drug, offering both developmental benefits and regulatory incentives. In this guide, we explore key strategic considerations for applying for Orphan Drug Designation and how BioBoston Consulting can support you through the process.
When Is the Right Time to Apply for Orphan Drug Designation?
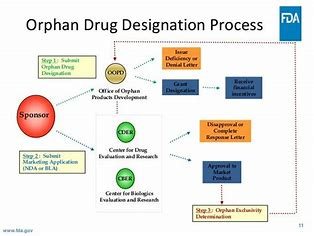
A common question among clinical trial sponsors is: When should we apply for Orphan Drug Designation? According to CFR 316.23, ODD can be requested at any point before submitting a marketing application. However, the timing of your application depends on various factorssuch as:
Key Strategic Considerations Before Pursuing Orphan Drug Designation
1. Assess the Prevalence of the Disease
To qualify for ODD, the disease must affect fewer than 200,000 individuals in the U.S. Review credible sources such as SEER (for oncology), NORD, or other relevant literature to ensure that your application is well-supported. If U.S.-specific data is unavailable, global data can be used, but make sure to reference it appropriately. Proactively addressing outliers in prevalence data will strengthen your case with the FDA.
2. Understand the Disease and Unmet Medical Need
A deep scientific understanding of the disease is mandatory. You must demonstrate how the current treatment landscape is insufficient and show how your drug can improve patient outcomes. The FDA will closely scrutinize the existing therapeutic gaps and how your treatment addresses them.
3. Demonstrate the Mechanism of Action
ODD applications must present clear evidence of how your drug impacts the biological pathways responsible for the orphan disease. Articulating the drug’s mechanism of action is a crucial component of the application and for ensuring that the FDA understands its potential therapeutic benefits.
4. Present Robust Supporting Data
Applications backed by solid clinical data from early-phase clinical results, animal models, or in vitro data are the most successful. While preclinical data may be accepted, it must convincingly demonstrate the drug’s potential. In some cases, in vitro data from human cell lines may be sufficient, but relying solely on in vitro data makes obtaining ODD more challenging.
5. Prepare for Additional FDA Inquiries
After submitting your ODD application, expect the FDA to review your submission within 90 days. They may request additional information or clarifications, and you should be prepared to generate further data or provide explanations for any data gaps.
Expediting Development After Receiving Orphan Drug Designation
Once ODD is granted, it is important to implement strategies that can accelerate clinical development, especially for orphan diseases, which may present recruitment challenges due to small patient populations.
1. Adopt a Patient-Centred Approach
Engaging with patient advocacy groups early in the process can offer valuable insights into patient needs and the outcomes that matter most. Understanding the natural history of the disease and incorporating patient-reported outcomes into clinical trials can streamline trial design and enhance its relevance.
2. Collaborate with Global Regulators
Establishing relationships with regulatory bodies beyond the FDA ensures that your clinical trial aligns with international expectations. This global approach can help refine study endpoints and optimize your drug’s path to approval.
3. Partner with Specialized CROs and Vendors
Partnering with experienced Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) specializing in orphan diseases is key to ensuring efficient trial execution. The use of digital health tools, AI, and machine learning can also facilitate patient recruitment and data collection for rare disease studies.
4. Identify Biomarkers Early
Leverage early nonclinical studies and patient data to identify potential biomarkers. These biomarkers will help you select the right patient populations, monitor disease progression, and assess treatment effectiveness. Early biomarker identification can speed up clinical development by avoiding unnecessary treatments for ineffective therapies.
Risks of Applying for Orphan Drug Designation Early
Applying for ODD early comes with some risks, including the possibility of rejection. However, FDA feedback can offer valuable guidance for refining and improving your submission. Rejections are not made public, and sponsors can use the feedback to strengthen their application for resubmission. While there is minimal financial risk since ODD applications have no fee, the reputational risk may be greater if a company has publicly committed to securing ODD within a specific timeline, especially for investors.
Conclusion: Strategic Timing for Orphan Drug Designation
The decision to pursue Orphan Drug Designation is a critical one that hinges on your drug’s development stage, available data, and strategic goals. By thoroughly understanding the disease and unmet medical need, providing robust scientific data, and engaging early with regulatory authorities, you can strengthen your chances of a successful ODD application.
BioBoston Consulting: Your Partner in Securing Orphan Drug Designation
Navigating the complexities of Orphan Drug Designation and rare disease clinical trials requires expertise and strategic guidance. BioBoston Consulting is here to help you optimize your ODD application and clinical development process. Our experienced team can assist in ensuring that your application aligns with FDA requirements and that your clinical trials are designed for success.
Ready to Secure Orphan Drug Designation? Contact BioBoston Consulting Today!
Let us help you fast-track your path to market with tailored strategies for Orphan Drug Designation. Contact BioBoston Consulting now and benefit from our expert guidance throughout your drug development journey.