“Explore critical upstream bioprocessing techniques such as cell culture, fermentation, and media optimization in biotechnology. Learn how bioreactors and fermentation methods improve product yield and quality in biopharmaceutical manufacturing.”
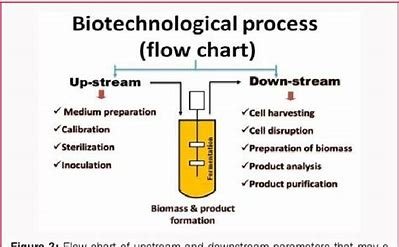
Explore the world of upstream bioprocessing techniques, highlighting some of the critical principles and optimization methods driving the biotechnology industry.
Cell Culture Techniques:
Adherent cultures ⇔ Suspension cultures: Adherent vs. suspension culture depends on the type of cells and also the nature of the produced products. While suspension cultures, in which cells are free floating in the medium, are favored for scalability, some cell types may lend themselves well to adherent cultures, whereby cells must bind to a surface.
Bioreactors
Bioreactors (a critical element of cell culture) manage and enclose the environment for cell growth. Bioreactors are diverse and can range from stirred-tank bioreactors, wave bioreactor to perfusion systems. The right system will depend on cell type, scalability, and the requirements of your process.
Fermentation Techniques:
Based on the mode of fermentation: The fermentation processes can be divided into batch, fed-batch, and continuous. Batch fermentation is single cyclenfed-batch,where nutrients can be added during the fermentation process. In this case, continuous fermentation provides constant state where the strength of productivity and resource use is heightened.
Aeration and agitation:
Aeration and agitation are essential for microbial growth, cell yield. When designing fermentation processes, it is imperative to consider factors affecting oxygen availability, mixing efficiency and shear stress on cells. Striking just the right balance means that microbes can work best.
Media Optimization:
Nutrient Composition:
Media optimization can provide bespoke nutrient compositions catering specifically to the needs of the cells/microorganisms such as the carbon sources, nitrogen sources, minerals and vitamins by optimizing the media for cell growth and productivity
Feed Strategies:
The use of varying feed strategies such as batch vs sequential feeding need to be implemented in a way that nutrient levels are maintained at optimal concentrations during the entire bioprocess. This can ensure that cell and product grow continuously.
Conclusion
The steps used in upstream bioprocessing are numerous and significant for the success of biomanufacturing. A large sector of the biopharmaceutical industry can benefit from improvements in product quality and yield as well by understanding cell culture, fermentation, and media optimization principles.
BioBoston Consulting has the firm belief to stimulate upstream bioprocessing amongst trailblazers of the industry and is looking forward to engage in partnership finding missions by providing grounded solutions. Join us as we continue to raise the bar for innovations in biomanufacturing.
Click BioBoston Consulting for contacting us or visit our website for more information on how we may assist your organisation.